

The output of the above application in action is given below.
#BUTTONBAR BUTTONSTYLE ANDROID CODE#
The code for the MainActivity.java class which hosts all of the above button examples is given below. Setting the Button shape as capsule btn_shape_capsule.xml is where we set the shape inside the selectors as a capsule. A linear gradient should have the angle specified in the multiples of 45, else it’ll crash. Set this on the Button and the shape would change from rectangle to oval when the button is clicked. The btn_selector_shape.xml holds the selector. Īndroid Button Shape and Selector Together We must set the gradient_radius attribute too. In the following btn_shape_gradient.xml file, we’ve set the gradient as a radial one. Just like selectors, we can set this on the android:background tag on the Button in our xml layout. The xml code for the btn_shape_round.xml file is given below: - Setting the solid color on the button.- Setting start and end colors of the gradient along with the type(radius, linear, sweep).The most used tags inside the shape tag are: The shape can be set to rectangle(default), oval, ring, line. These xml files are created in the drawable folder too. We can set custom shapes on our button using the xml tag. We need to use android:color here in place of android:drawable. The following code from btn_txt_selector.xml does so. We can change the text color on the button based on the state in the selector. ImageButton comes with the android:scale attribute to resize the drawable image. ImageButton is the ideal View to be used when you need to display a drawable as the button background only since it fits the drawable appropriately. For the sake of convenience we’ve done the former here: We can do so either by hardcoding in xml or getting the drawable dimensions programmatically and setting it over the button. So we need to set the Button width/height in accordance with the drawable image.
Now the drawable images when set as the button background can get stretched if it’s width/height is larger than the button’s. Note: The focused state doesn’t work on smart phones. The selector code that does so is present in the file btn_drawable_selector.xml We can set a different drawable image to be displayed based upon the state of the button. įor the above selector to work, we need to specify android:enabled as false. The following selector btn_bg_selector_disabled.xml is used on a button which is not enabled. The selector is set on the background attribute of the button. We set the above drawable selector file on our button in the activity_main.xml as: Keeping it at the top would not allow the other two item tags to get executed ever. It’s important that we keep it at the last. Whenever the condition matches, it sets the relevant things on the button and stops processing the next item tags. It checks every condition from top to bottom. The selector tag behaves like an if - else if statement to an extent. In the above code, each of the states is represented using item tag. The following selector file btn_bg_selector.xml contains the code for setting different background colors on a button for different states. Selector for different background colors. The colors are defined in the colors.xml file : A selector can be an xml file created inside the drawable folder. We’ll be looking at each of the drawable files one at a time.
#BUTTONBAR BUTTONSTYLE ANDROID ANDROID#
Let’s get started with the implementation of each of these in a new Android Studio Project. For each of the states of the selector, we can set a different drawable/color/shape on our button. Typically for a button, there are just three important states: normal, pressed and enabled. state_selected is meant to select the view. State_focused is when you hover over the widget. What are drawable states? Each of the following events of a view (Button or any other kind of view) are a type of state:
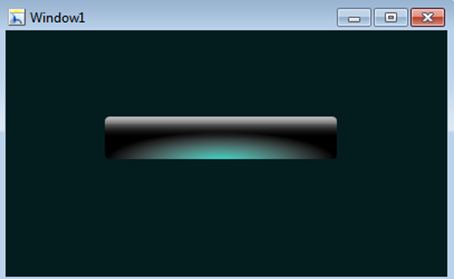
Android Button DesignĪ selector is used to define a different behaviour for different states of the Button.

We’ll be setting selectors and shapes on our buttons in xml. If you aren’t aware of Android Buttons, check out this tutorial before proceeding. In this tutorial, we’ll be customizing the Buttons in our Android Application.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
